前言
http协议是互联网上使用最广泛的通讯协议了。Web通讯也是基于http协议;对应c#开发者来说ASP.NET Core是最新的开发Web应用平台。
由于最近要开发一套人脸识别系统,对通讯效率的要求很高。虽然.NET Core对http处理很优化了,但是我决定开发一个轻量级http服务器;不求功能多强大,只求能满足需求,性能优越。本文以c#开发windows下http服务器为例。
经过多年的完善、优化,我积累了一个非常高效的网络库《.NET中高性能、高可用性Socket通讯库》以此库为基础,开发一套轻量级的http服务器难度并不大。花了两天的时间完成http服务器开发,并做了测试。
同时与ASP.NET Core处理效率做了对比,结果出乎意料。我的服务器性能是ASP.NET Core的10倍。对于此结果一开始我也是不相信,经过多次反复测试,事实却是如此。此结果并不能说明我写的服务器优于ASP.NET Core,只是说明一个道理:合适的就是最好,高大上的东西并不是最好的。
1、HTTP协议特点
HTTP协议是基于TCP/IP之上的文本交换协议。对于开发者而言,也属于socket通讯处理范畴。只是http协议是请求应答模式,一次请求处理完成,则立即断开。http这种特点对sokcet通讯提出几个要求:
a)、能迅速接受TCP连接请求。TCP是面向连接的,在建立连接时,需要三次握手。这就要求socket处理accept事件要迅速,要能短时间处理大量连接请求。
b)、服务端必须采用异步通讯模式。对windows而言,底层通讯就要采取IOCP,这样才能应付成千上万的socket请求。
c)、快速的处理读取数据。tcp是流传输协议,而http传输的是文本协议;客户端向服务端发送的数据,服务端可能需要读取多次,服务端需要快速判断数据是否读取完毕。
以上几点只是处理http必须要考虑的问题,如果需要进一步优化,必须根据自身的业务特点来处理。
2、快速接受客户端的连接请求
采用异步Accept接受客户端请求。这样的好处是:可以同时投递多个连接请求。当有大量客户端请求时,能快速建立连接。
异步连接请求代码如下:
public bool StartAccept()
{
SocketAsyncEventArgs acceptEventArgs = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
acceptEventArgs.Completed += AcceptEventArg_Completed;
bool willRaiseEvent = listenSocket.AcceptAsync(acceptEventArgs);
Interlocked.Increment(ref _acceptAsyncCount);
if (!willRaiseEvent)
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _acceptAsyncCount);
_acceptEvent.Set();
acceptEventArgs.Completed -= AcceptEventArg_Completed;
ProcessAccept(acceptEventArgs);
}
return true;
}
可以设置同时投递的个数,比如此值为10。当异步连接投递个数小于10时,立马再次增加投递。有一个线程专门负责投递。
_acceptAsyncCount记录当前正在投递的个数,MaxAcceptInPool表示同时投递的个数;一旦_acceptAsyncCount小于MaxAcceptInPool,立即增加一次投递。
private void DealNewAccept()
{
try
{
if (_acceptAsyncCount <= MaxAcceptInPool)
{
StartAccept();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_log.LogException(0, "DealNewAccept 异常", ex);
}
}
3、快速分析从客户端收到的数据
比如客户端发送1M数据到服务端,服务端收到1M数据,需要读取的次数是不确定的。怎么样才能知道数据是否读取完?
这个细节处理不好,会严重影响服务器的性能。毕竟服务器要对大量这样的数据进行分析。
http包头举例
POST / HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Content-Type: application/x-www-from-urlencoded
Host: www.163.com
Content-Length: 7
Connection: Keep-Alive
body
分析读取数据,常规、直观的处理方式如下:
1) 、将收到的多个buffer合并成一个buffer。如果读取10次才完成,则需要合并9次。
2) 、将buffer数据转成文本。
3) 、找到文本中的http包头结束标识("\r\n\r\n") 。
4) 、找到Content-Length,根据此值判断是否接收完成。
采用上述处理方法,将严重影响处理性能。必须另辟蹊径,采用更优化的处理方法。
优化后的处理思路
1、多缓冲处理
基本思路是:收到所有的buffer之前,不进行buffer合并。将缓冲存放在List<byte[]> listBuffer中。通过遍历listBuffer来查找http包头结束标识,来判断是否接收完成。
类BufferManage负责管理buffer。
public class BufferManage
{
List<byte[]> _listBuffer = new List<byte[]>();
public void AddBuffer(byte[] buffer)
{
_listBuffer.Add(buffer);
}
public bool FindBuffer(byte[] destBuffer, out int index)
{
index = -1;
int flagIndex = 0;
int count = 0;
foreach (byte[] buffer in _listBuffer)
{
foreach (byte ch in buffer)
{
count++;
if (ch == destBuffer[flagIndex])
{
flagIndex++;
}
else
{
flagIndex = 0;
}
if (flagIndex >= destBuffer.Length)
{
index = count;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int TotalByteLength
{
get
{
int count = 0;
foreach (byte[] item in _listBuffer)
{
count += item.Length;
}
return count;
}
}
public byte[] GetAllByte()
{
if (_listBuffer.Count == 0)
return new byte[0];
if (_listBuffer.Count == 1)
return _listBuffer[0];
int byteLen = 0;
_listBuffer.ForEach(o => byteLen += o.Length);
byte[] result = new byte[byteLen];
int index = 0;
foreach (byte[] item in _listBuffer)
{
Buffer.BlockCopy(item, 0, result, index, item.Length);
index += item.Length;
}
return result;
}
public byte[] GetSubBuffer(int start, int countTotal)
{
if (countTotal == 0)
return new byte[0];
byte[] result = new byte[countTotal];
int countCopyed = 0;
int indexOfBufferPool = 0;
foreach (byte[] buffer in _listBuffer)
{
//找到起始复制点
int indexOfItem = 0;
if (indexOfBufferPool < start)
{
int left = start - indexOfBufferPool;
if (buffer.Length <= left)
{
indexOfBufferPool += buffer.Length;
continue;
}
else
{
indexOfItem = left;
indexOfBufferPool = start;
}
}
//复制数据
int dataLeft = buffer.Length - indexOfItem;
int dataNeed = countTotal - countCopyed;
if (dataNeed >= dataLeft)
{
Buffer.BlockCopy(buffer, indexOfItem, result, countCopyed, dataLeft);
countCopyed += dataLeft;
}
else
{
Buffer.BlockCopy(buffer, indexOfItem, result, countCopyed, dataNeed);
countCopyed += dataNeed;
}
if (countCopyed >= countTotal)
{
Debug.Assert(countCopyed == countTotal);
return result;
}
}
throw new Exception("没有足够的数据!");
// return result;
}
}
类HttpReadParse借助BufferManage类,实现对http文本的解析。
public class HttpReadParse
{
BufferManage _bufferManage = new BufferManage();
public void AddBuffer(byte[] buffer)
{
_bufferManage.AddBuffer(buffer);
}
public int HeaderByteCount { get; private set; } = -1;
string _httpHeaderText = string.Empty;
public string HttpHeaderText
{
get
{
if (_httpHeaderText != string.Empty)
return _httpHeaderText;
if (!IsHttpHeadOver)
return _httpHeaderText;
byte[] buffer = _bufferManage.GetSubBuffer(0, HeaderByteCount);
_httpHeaderText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer);
return _httpHeaderText;
}
}
string _httpHeaderFirstLine = string.Empty;
public string HttpHeaderFirstLine
{
get
{
if (_httpHeaderFirstLine != string.Empty)
return _httpHeaderFirstLine;
if (HttpHeaderText == string.Empty)
return string.Empty;
int index = HttpHeaderText.IndexOf(HttpConst.Flag_Return);
if (index < 0)
return string.Empty;
_httpHeaderFirstLine = HttpHeaderText.Substring(0, index);
return _httpHeaderFirstLine;
}
}
public string HttpRequestUrl
{
get
{
if (HttpHeaderFirstLine == string.Empty)
return string.Empty;
string[] items = HttpHeaderFirstLine.Split(' ');
if (items.Length < 2)
return string.Empty;
return items[1];
}
}
public bool IsHttpHeadOver
{
get
{
if (HeaderByteCount > 0)
return true;
byte[] headOverFlag = HttpConst.Flag_DoubleReturnByte;
if (_bufferManage.FindBuffer(headOverFlag, out int count))
{
HeaderByteCount = count;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
int _httpContentLen = -1;
public int HttpContentLen
{
get
{
if (_httpContentLen >= 0)
return _httpContentLen;
if (HttpHeaderText == string.Empty)
return -1;
int start = HttpHeaderText.IndexOf(HttpConst.Flag_HttpContentLenth);
if (start < 0) //http请求没有包体
return 0;
start += HttpConst.Flag_HttpContentLenth.Length;
int end = HttpHeaderText.IndexOf(HttpConst.Flag_Return, start);
if (end < 0)
return -1;
string intValue = HttpHeaderText.Substring(start, end - start).Trim();
if (int.TryParse(intValue, out _httpContentLen))
return _httpContentLen;
return -1;
}
}
public string HttpAllText
{
get
{
byte[] textBytes = _bufferManage.GetAllByte();
string text = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(textBytes);
return text;
}
}
public int TotalByteLength => _bufferManage.TotalByteLength;
public bool IsReadEnd
{
get
{
if (!IsHttpHeadOver)
return false;
if (HttpContentLen == -1)
return false;
int shouldLenth = HeaderByteCount + HttpContentLen;
bool result = TotalByteLength >= shouldLenth;
return result;
}
}
public List<HttpByteValueKey> GetBodyParamBuffer()
{
List<HttpByteValueKey> result = new List<HttpByteValueKey>();
if (HttpContentLen < 0)
return result;
Debug.Assert(IsReadEnd);
if (HttpContentLen == 0)
return result;
byte[] bodyBytes = _bufferManage.GetSubBuffer(HeaderByteCount, HttpContentLen);
//获取key value对应的byte
int start = 0;
int current = 0;
HttpByteValueKey item = null;
foreach (byte b in bodyBytes)
{
if (item == null)
item = new HttpByteValueKey();
current++;
if (b == '=')
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[current - start - 1];
Buffer.BlockCopy(bodyBytes, start, buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
item.Key = buffer;
start = current;
}
else if (b == '&')
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[current - start - 1];
Buffer.BlockCopy(bodyBytes, start, buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
item.Value = buffer;
start = current;
result.Add(item);
item = null;
}
}
if (item != null && item.Key != null)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[bodyBytes.Length - start];
Buffer.BlockCopy(bodyBytes, start, buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
item.Value = buffer;
result.Add(item);
}
return result;
}
public string HttpBodyText
{
get
{
if (HttpContentLen < 0)
return string.Empty;
Debug.Assert(IsReadEnd);
if (HttpContentLen == 0)
return string.Empty;
byte[] bodyBytes = _bufferManage.GetSubBuffer(HeaderByteCount, HttpContentLen);
string bodyString = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bodyBytes);
return bodyString;
}
}
}
4、性能测试
采用模拟客户端持续发送http请求测试,每个http请求包含两个图片。一次http请求大概发送70K数据。服务端解析数据后,立即发送应答。
注:所有测试都在本机,客户端无法模拟大量http请求,只能做简单压力测试。
1)本人所写的服务器,测试结果如下
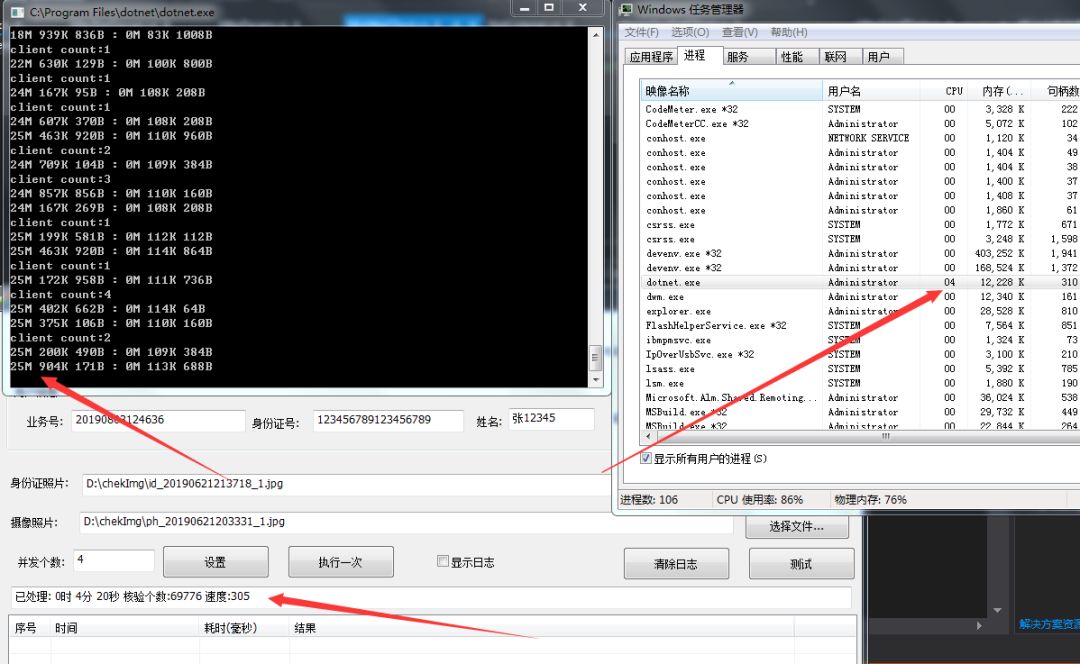
每秒可发送300次请求,每秒发送数据25M,服务器cpu占有率为4%。
2)ASP.NET Core 服务器性能测试

每秒发送30次请求,服务器cpu占有率为12%。
测试对比
本人开发的服务端处理速度为ASP.NET Core的10倍,cpu占用为对方的三分之一。ASP.NET Core处理慢,有可能实现了更多的功能;只是这些隐藏的功能,对我们也没用。
后记
如果没有开发经验,没有清晰的处理思路,开发一个高效的http服务器还有很困难的。
本人也一直以来都是采用ASP.NET Core作为http服务器。因为工作中需要高效的http服务器,就尝试写一个。
不可否认,ASP.NET Core各方面肯定优化的很好;但是ASP.NET Core 提供的某些功能是多余的。如果化繁为简,根据业务特点开发,性能未必不能更优。
该文章在 2025/7/2 16:58:15 编辑过